Table of Contents
Devices intended for surgical cutting and for controlling bleeding by causing coagulation (hemostasis) at the surgical site. Electrosurgery is commonly used in dermatological, gynecological, cardiac, plastic, ocular, spine, ENT, maxillofacial, orthopedic, urological, neuro- and general surgical procedures as well as certain dental procedures.
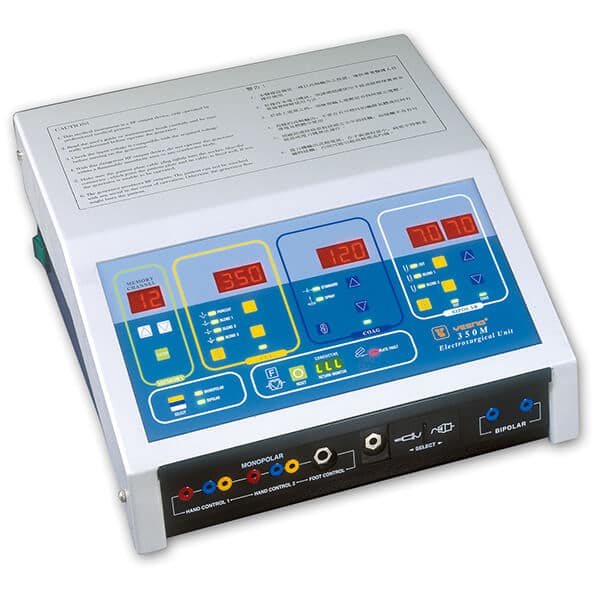
What’s an electrosurgical unit?
High-frequency
Electrosurgery is a procedure that involves use of high-frequency (100 kilohertz – 5 megahertz) for performing surgery. In this approach electric current (200–10,000 Volts) with alternating polarity acts as a means to target biological tissues, for example, coagulation, fulguration, cutting and fulguration. The main advantage of using electrosurgery is that it helps to make precise cuts with minimal loss of blood. Electrosurgical units are frequently used in hospitals to improve effectiveness of surgical operations. High frequency electric current is passed through the target area which generates heat.
Components
An electrosurgical unit (ESU) consists of important components, including a generator and a handpiece. The handpiece has one or more electrodes depending on its purpose. A switch on the handpiece or a foot switch provides control to manage the device. Different electrical waveforms can occur with the use of electrosurgical generators. Depending on the requirement and tissue effects, the waveform also change. Several variations of electrical hemostasis include electrofulguration, electrodesiccation, electrocautery, and electrocoagulation. Others types of electrosurgery are electrolysis and electrosection.
What are different types of electrosurgical units?
There are different kinds of electrosurgical units available in the market. The sources of energy vary for these, and based on the mechanism they are categorized.
- High frequency surgical units: This surgical unit transforms current into high frequency current (> 200 kHZ). It is commonly known as radio frequency surgical units.

- Molecular resonance surgical units: They work in a unique manner as they use frequencies that show biological effects in a non-thermal manner. As only molecular changes take place hence they are less-invasive in nature.
- Ultrasound surgical unit: Ultrasonic handpiece use these kind of surgical units. With the help of ultrasound waves tissue undergoes coagulation and cavitation. Ultrasonic wave generator breaks the hydrogen bonds at a cellular level that provides adequate hemostasis.
What are different modes of using electrosurgical unit?
The electrosurgery device has two common modes which includes monopolar and bipolar electrodes.
Bipolar electrosurgery
- Bipolar electrosurgery: This refers to the surgical unit where both the active electrode and return electrode activities occur at the surgical site. The tips of the forceps conduct these two functions. The tissue grasped between the forceps is included within the electric circuit. It does not require any additional patient return electrode as the function is managed by one tip of the forceps. It has an important benefit of operating in any environment irrespective of the medium. For example, even in a wet/fluid field, coagulation is possible. Hence, also referred as ‘wet field’ cautery.
Monopolar electrosurgery
- Monopolar electrosurgery: This type of device consist of two kinds of electrodes: active electrode which is used at the site of surgery, and patient return electrode which is placed on the patient’s body. Other name for patient return electrode is dispersive pad. As the current passes from the active electrode to the patient return electrode, the circuit gets completed. Patient return electrode maintains patient safety.
What are the different modalities used in electrosurgery?
- Cutting mode: This mode helps to vaporize water content from the tissues. Due to high voltage the water becomes vapor once the electrode touches the tissue. Vapor and other fragments are removed forming a crater.
- Coagulation mode: In this mode, lower power is used as the main aim is to coagulate the tissue instead of vaporization
- Desiccation mode: When the electrode touches the tissue exposed to air, high amount of heat is generated which is lower than that needed for cutting. It is generally a suitable option in cases for treating nodules so that minimal damage occurs to the skin.
- Fulguration mode: In this method the electrode remains at a distance from the tissue as a result the air between the tissue and electrode gets ionized. This causes an electric arc discharge. The current is spread over a larger surface area and not limited to the tip of electrode which results in superficial burning of the tissue. Superficial charring or carbonization occurs due to heat distribution instead of heat limited to the tip of the probe.
- Electroporation: Electrosurgery may lead to formation of pores in the cellular membranes. The cellular structure changes beyond the range of thermal damage.
What are the factors that affect the efficiency of electrosurgical unit?
There are certain key factors that influence the performance of ESU which includes:
- Current density: Higher current density results in greater effects on the tissue.
- Time: A longer activation period will have a wider and deeper effect on tissue, while less activation time will result in superficial and less desirable outcome.
- Electrode size: Smaller electrode size limits the spread of heat and causes greater impact on the tissue
- Tissue conductivity of the tissue: Rate of heating is influenced by the electrical resistance of the tissue. For example, muscle and skin are good conductors of current whereas bone and adipose tissue are poor conductors of current.
What things should be considered while using electrosurgical units?
The device generates high amount of heat and high current which may cause injury to the patient and operator if mishandled. Studies have shown that problems such as burns at the placement of patient return electrode and surgical fires may occur. It becomes important to be careful and take necessary precautions while using them:
Dos
- Keep the handpiece in thenonconductive holster if you are not using it.
- Maitain a suitable or low generator setting to achieve desirable surgical effects. Higher voltage may lead to an increased risk of arching. Higher settings also disrupts the integrity of the dispersive pads and skin interface.
- Electrode tip should be cleaned frequently. Due to eschar accumulation on the tip, the risk of sparking and flaming of the eschar also increases. This ignition takes place due to higher electrical impedance which causes arching.
- A sponge is helpful for cleaning the electrode and removing the eschar.
- Avoid using scratch pads for wiping away the eschar as it may cause scratch on the electrodes, promoting eschar build-up.
Don’ts
- Do not use ESUs in the presence of any flammable material or in oxygen-rich environments. For example, if flammable substances such as alcohol is being used before surgical procedure make sure to prevent the use of alcohol-based skin preps near the dispersive pads. The area should be dry before activating ESU.
- Do not operate electrosurgical equipment when hands are wet or with wet gloves.
- Always wear intact gloves as holes in the surgical gloves will allow electrical current to pass through them.
- Never use ESU while standing on a wet surface. The foot pedal should be dry. A clear, waterproof cover will help to protect the pedal from any fluid spillage.
What are the Indication of electrosurgical unit?
- Electrosurgery has become popular among all the clinicians. Commonly used to cut, ablate, coagulate, shrink, dissect and fulgurate the tissues in all types of medical field. It is beneficial in the management of actinic keratosis, eye surgery, hemostasis for bleeding, small angiomas, and seborrheic keratosis.
- Electrocoagulation helps to treat different chronic conditions such as verruca vulgaris, basal cell carcinoma, angiofibromas, sebaceous hyperplasia, ingrown toenail matrixectomy, squamous cell carcinoma, Bowen’s disease and hemostasis for arterial bleeding.
- Electrosection provides effective treatment in skin conditions involving incision and excision. This includes rhinophyma repair, acne keloidalis nuchae, scar revision, blepharoplasty incision, shave removal, skin-flap undermining, incisions and resurfacing.
- ESU helps in achieving rapid hemostasis compared to a scalpel. Although, the device produces smoke and plumes but if used carefully it leads to a quick, precise and an effortless surgery.
What are the contraindications of electrosurgical unit?
Patients with cardiac devices should be operated carefully where short bursts of energy are used (<5 seconds). It is recommended that low power settings works well and the area around the cardiac device should be avoided. Limit the use to a smaller area so that current is targeted to that specific site such as by the use of bipolar forceps. Although, no particular case of interference with a pacemaker has been reported, but to minimize any complications in future these suggestions are advised.
Conclusion
Hence, based on the different types of modes, applications and desired tissue effects ESU can be selected. They are not only used in dermatology for cosmetic purpose but gaining popularity for the treatment of severe and aggressive medical conditions. Some of the uses are removal of benign or malignant tumors, and acne keloidalis nuchae. Treatment of skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell in situ by electrodesiccation and curettage. Based on the patient’s requirements, the selection of ESU is done to achieve best patient outcome while conducting the surgical procedure.