Table of Contents
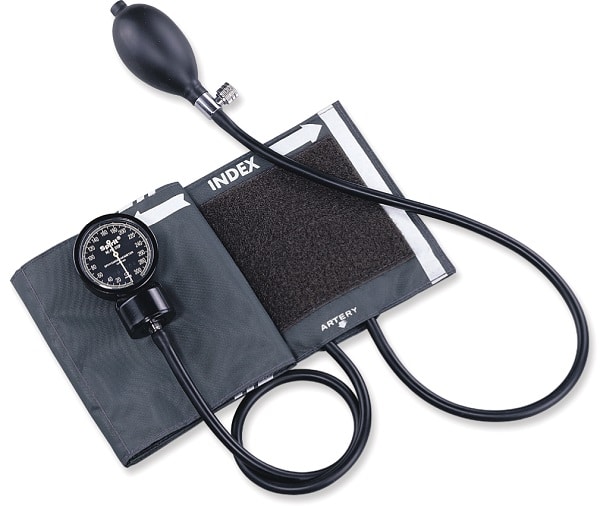
A sphygmomanometer is a device which helps to measure blood pressure. It is also known as blood pressure gauge or blood pressure monitor. It consist of an inflatable cuff that exerts pressure and then releases the artery under the cuff in a systematic manner. Blood pressure is monitored with the changes in mercury and aneroid manometer.
Typically, in manual sphygmomanometers a stethoscope is used when using an auscultatory technique.
So, in total a sphygmomanometer consists of these components:
- An inflatable cuff
- A measuring unit: Mercury manometer or aneroid gauge
- Mechanism of inflation: Manually operated bulb or an electrically operated pump.

What are the different types of sphygmomanometer?
Manual sphygmomanometers
In this method, a stethoscope is used for conducting auscultation. Commonly, any trained clinician can use manual meters and obtain a basic reading through palpation, although it only provides systolic pressure.
- Mercury sphygmomanometers are widely used and considered as the gold standard. It does not require any recalibration as pressure is indicated by a column of mercury.
- Manual sphygmomanometers are accurate and therefore popularly used in clinical trials of drugs and in clinical assessment of high-risk patients such as pregnant women.
- Baumanometer is a commonly used wall mounted mercury sphygmomanometer.
- Another variety is aneroid sphygmomanometers that is a mechanical type with a dial. It usually requires calibration checks unlike mercury manometers. They are safer than manual ones, although inexpensive ones can be less accurate
- Mechanical jarring is the most common reason causing departure from calibration.
Digital sphygmomanometers
Digital meters do not use auscultatory techniques, and are based on oscillometric measurements and electronic calculations. It can use either automatic or manual inflation, however both are electronic and are simple and easy to use. It does not require any special training and can be used in a noisy environment.
- These are important as they can measure both systolic and diastolic pressures through oscillometric methods. It can detect mean blood pressure and pulse rate but the blood pressure is less accurate compared to manual meters and calibration is also inadequate.
- Digital monitors should be avoided by certain patients, especially those suffering from conditions such as pulsus paradoxus, arteriosclerosis, arrhythmia, pulsus alternans and preeclampsia. As the calculation may be incorrect in these medical conditions hence it is not advised to assess the blood pressure through digital oscillometric monitors. In these situations, an analog sphygmomanometer can be used by a trained professional.
- A recent development occurred wherein a smartphone based device based on oscillometry was used to estimate blood pressure.
- The method of detecting blood pressure between the oscillometric method and auscultatory approach can depend on several factors such as heart rate, arterial stiffness, and pulse pressure
- Some believe that certain instruments can also measure arterial stiffness and assess irregular heartbeats.
What are the factors that affect the blood pressure measurement?
There are several critical factors that may impact the reading of blood pressure, especially from the upper arm.
Effects of posture
- There is no well-defined guidelines defining the most suitable posture for assessing blood pressure. It can be measured in a sitting or standing position, however mostly sitting is recommended.
- A study included 245 participants of different age group, it was found that systolic pressure were similar in both the positions. But, with respect to diastolic pressure a systematic age-related discrepancy was observed. It showed that people who belonged to age group of 30 had a sitting diastolic pressure 10mm higher compared to supine position. On the other hand, at the age of 70 the variation was only 2mm Hg.
Body position
- shifts the position from horizontal to vertical position, the blood pressure also increases by 5-6mm Hg. This shows that changes in the hydrostatic pressure leads to change in the blood pressure.
- While measuring blood pressure, the patient’s back should be supported adequately. If the patient is sitting upright then the diastolic pressure may be higher to up to 6.5mm than if sitting back.
Cuff-inflation hypertension
- Generally, inflating a sphygmomanometer cuff does not changes the blood pressure but in certain situations it may result in a transient, and substantial increase of about 40 mm Hg which coincides with the cuff inflation. This increase in blood pressure should be differentiated from white coat hypertension where the rise in blood pressure is seen before and after the act of inflation.
- In addition, it should also be differentiated from an increase in BP as seen during self-measurement which occurs due to muscular activity of inflating the cuff.
Appropriate cuff size
- It is important to select the size of a cuff which is in accordance with diameter of the arm. A small cuff size will result in overestimation of BP. Hence, it is recommended to use a large adult sized cuff that measures the BP correctly.
- According to the British Hypertension Society (BHS), if the arm circumference is more than 33 cm, then a large adult size cuff should be used (width 12.5 to 13 cm, length 35 cm).
What is the significance of self-monitoring of blood pressure by electronic monitors?
Initially aneroid sphygmomanometers were most commonly used but with recent advances several new home monitoring devices have been developed. Automatic electronic devices are gaining a lot of popularity as they provide self-monitoring of blood pressure. The important ones are mentioned below:
- Wrist monitors: They have monitors which are smaller in size than the arm devices and can be used in obese individuals. As the size of wrist is not greatly affected due to obesity. The main disadvantage of wrist monitors is that they can have systematic error due to difference in wrist position relative to the heart. If they are placed at the heart level while readings are taken then this error can be avoided
- Finger monitors: These monitors are simple and easy to use but the main challenge observed with them is inaccurate results and thus they should be avoided.
- Manual models: Manual sphygmomanometers are most widely used by clinicians. They provide accurate results, although a thorough procedure should be followed while using them.
- Cuff-mounted: These type of sphygmomanometers are helpful as they provide accurate results. They do not generally impose constraint for doctors as they do not have to bear the weight of the pressure gauge on the bulb. On the contrary, the weight has to be borne by the patient’s arm. This means that it can become difficult to use for elderly and babies.
- Hand-held: These are more comfortable to use by the patient as it consist of lighter cuffs. It can be easily changed and easier to be put on the patient. The cuff can be replaced easily if it gets worn out.
What are recent technologies and advancements?
Ambulatory monitors
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring was first developed four decades ago and is now currently gaining a lot of attention as a clinically useful technique. With advancement in technology different methods were introduced including small monitors that are relatively quiet and can measure 100 readings of BP in a span of 24 hours as the patient manages their day to day activities.
- They are more accurate when the patient is lying down compared to that when they are engaged in a physical activity.
- It can detect three variations of BP including the diurnal variation, the average level and short-term variability.
- It is observed that in hypertensive patients the average ambulatory pressure can be less compared to clinic pressure, whereas in some in can be within the normal range, resulting in white coat hypertension.
- This shows that due to difference in clinic and ambulatory pressure, the risk involvement will also be different.
Connected electronic blood pressure monitors
Connected electronic blood pressure monitors are becoming widely popular and are a successful tool for self-measurement.
- They are simple, easy to use, and compact and allow transfer of data via Bluetooth or wifi to a smartphone, personal computer or tablet.
- This highlights that they maintain a thorough follow-up and ensure adequate care is provided to the patient. If required the information can also be shared with the clinician.
- A regular tracking of patient’s BP, and progress in regularity of BP is also provided with the electronic BP.
- Self-monitoring develops a habit of maintaining a track of blood pressure and ensures it is within normal limits.
Conclusion
Sphygmomanometer is an important device that measures blood pressure. There are several varieties available, including manual and digital which have their own unique features and advantages. Although, manual approach is more accurate and effective in giving blood pressure readings but digital monitor are easy, simple and allow self-monitoring of blood pressure regularly. Selection of sphygmomanometer should be done after assessing their unique features, needs and requirements.